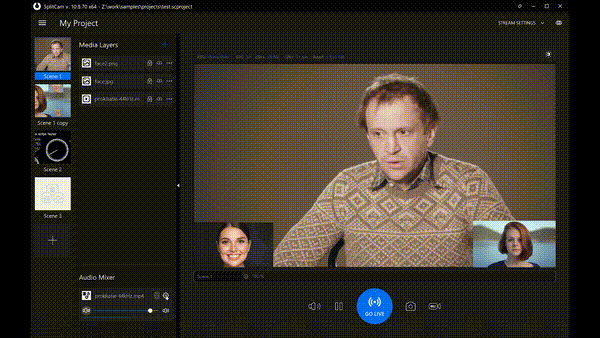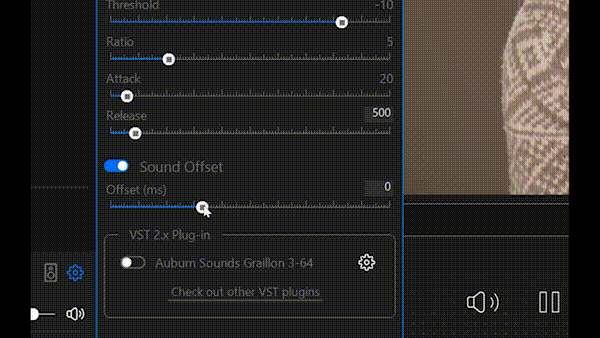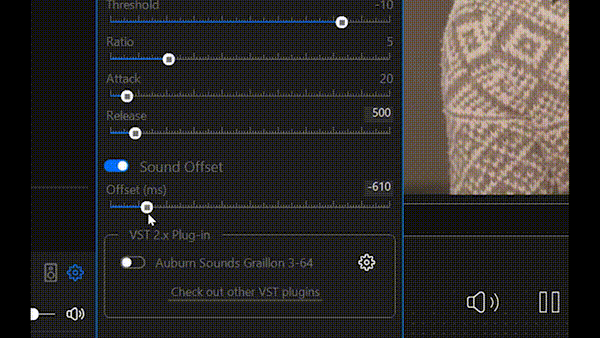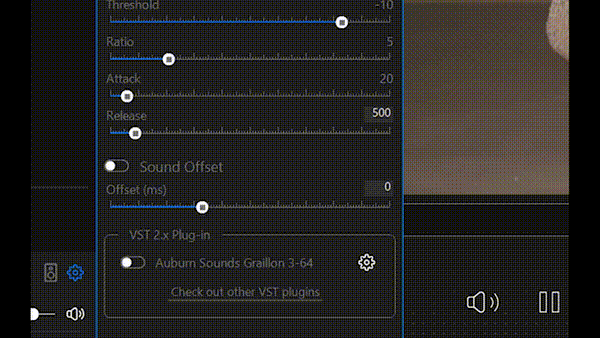
This document highlights changes to #SplitCam software since May to December, 2025. The latest version of SplitCam at this point is v10.8.70.
Over the course of this development period, we have introduced a wide range of new features and visual effects aimed at significantly expanding the capabilities of the application. These improvements are designed to enhance usability, flexibility, and creative freedom, and we are confident that they will provide clear value to our users in their everyday workflows.
Several of the newly added features are unique to SplitCam and distinguish it from similar solutions. These include location-based supporting web services, which automatically select the most suitable server depending on the user’s region, as well as automatic text layer translation, allowing users to create multilingual content by entering text in their native language and displaying it in the selected target language.
In addition, we have expanded the set of available scene and layer effects, providing users with more tools for visual composition, animation, and synchronization. These effects offer greater control over how content is presented and enable users to implement a wider range of creative ideas without relying on external software.
Due to the technical complexity of some tasks and existing resource constraints, not all planned work could be completed by the end of the year. However, these items remain part of our roadmap, and we plan to finalize them in the next development cycle.
The Sound Offset audio filter adds a configurable time delay to the audio track relative to the video. It allows shifting audio playback forward or backward in time without affecting pitch or playback speed, changing only the synchronization between audio and video streams.
This filter is primarily used to correct audio–video synchronization issues in video files, for example when sound is heard earlier or later than the corresponding visual events. Such issues commonly occur due to differences in audio and video capture latency, processing delays, or transcoding artifacts. Use it to precisely align the audio track with the video, ensuring correct lip-sync and a more natural viewing experience.
The Video Delay effect adds a configurable time delay to the video stream at the rendering stage. It shifts video playback relative to audio without altering frame rate or visual content, affecting only the timing of video presentation.
This effect is used to correct audio–video synchronization issues in scenarios where video is delayed or arrives earlier than audio, such as when video is captured from a webcam while audio is captured from a microphone with different processing latencies. Users can align the video stream with the audio track, ensuring proper lip-sync and consistent audiovisual synchronization.
The Scroll effect can be applied to an individual layer or to the entire scene. It continuously moves the visual content within the selected layer or scene horizontally and/or vertically, creating a scrolling motion.
This effect is commonly used to produce dynamic backgrounds, animated overlays, or continuous movement within a scene without modifying the underlying source content. By adjusting the horizontal and vertical scroll parameters, users can control the direction and speed of the scrolling, allowing for flexible visual composition and motion design.
The Fading Edges effect is applied to an individual layer and gradually fades its edges. It is designed to enable seamless blending of two or more separate layers placed within a scene.
This effect is useful when combining multiple videos or images into a single composite view, helping to eliminate hard borders and visible seams between adjacent layers. By softening the transitions at the edges of each layer, Fading Edges creates a smooth, cohesive visual result without abrupt boundaries or noticeable transitions.
The Show/Hide Layer Transitions effect is applied to an individual layer and is triggered when the user makes the layer visible or hides it from the scene. It controls how the layer appears and disappears during visibility changes.
This transition effect is used to smooth the visual change when a layer is enabled or disabled, avoiding abrupt on/off switching that can be distracting for the viewer. By adding a gradual transition to visibility changes, Show/Hide Layer Transitions makes scene composition more polished and visually pleasing.
AI Assistant is a new feature in the application that uses artificial intelligence to answer user questions related to working with SplitCam. It provides contextual guidance and help based on user requests. This feature helps users find solutions to specific tasks more quickly and navigate the application interface more efficiently.
The new Text Layer Translation feature allows automatic translation of text within a text layer on the scene. Users can enter text in their native language while the application translates and displays it in the selected target language. This functionality simplifies multilingual content creation and enables users to present text in different languages without manually rewriting or duplicating text layers.

New features for users in different regions. We have expanded the availability of the restream server to support users located in additional countries, including Russia. This improves access to restreaming functionality for a broader user base.
For users in Russia, support for the Remote Camera source has also been updated. This source enables users to transmit both video and audio from a smartphone directly into a live stream running in the SplitCam application, allowing more flexible streaming setups.
To ensure optimal performance, a dedicated server for users in Russia is hosted within the country. This minimizes latency and provides faster, more reliable connections when using restreaming and remote camera features.